According to the U.S. News & World Report, the DASH diet was ranked as the “best diet all around” for the eighth year in a row. Because DASH stands for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, its goal is focused on eating foods that help decrease blood pressure and reduce heart disease risk.
Complicated acronym aside, it is precisely what most nutrition experts have been preaching all along:

Before we dive into DASH, here’s why it matters in the first place.
BLOOD PRESSURE 101
Your heart pumps blood, oxygen and other nutrients to every cell in your body. When it contracts or relaxes, blood moves along the blood vessel walls exerting a force your doctor measures with a blood pressure cuff. A healthy, normal blood pressure is about 120 mmHg/80 mmHg or less.
You want blood pressure to be just right: high enough to circulate blood efficiently, but low enough that it doesn’t damage delicate blood vessel walls. Experts agree that high blood pressure, which affects 1 in every 3 adults, increases your risk for heart attack or stroke. Factors that affect blood pressure include weight, stress, hydration, activity level, temperature and diet.
READ MORE > ESSENTIAL GUIDE TO LOSING WEIGHT
THE DASH EATING PLAN
The DASH eating plan calls for less sodium, saturated fat and added sugar and more potassium, calcium, magnesium, fiber and lean protein. The theory is these nutrients work together synergistically to regulate blood pressure. Even if you’re already taking high blood pressure medications, following this eating plan can enhance your success.
Check out this chart for a daily breakdown of DASH macronutrient and micronutrient goals. You can enter these goals into the MyFitnessPal app and start tracking:
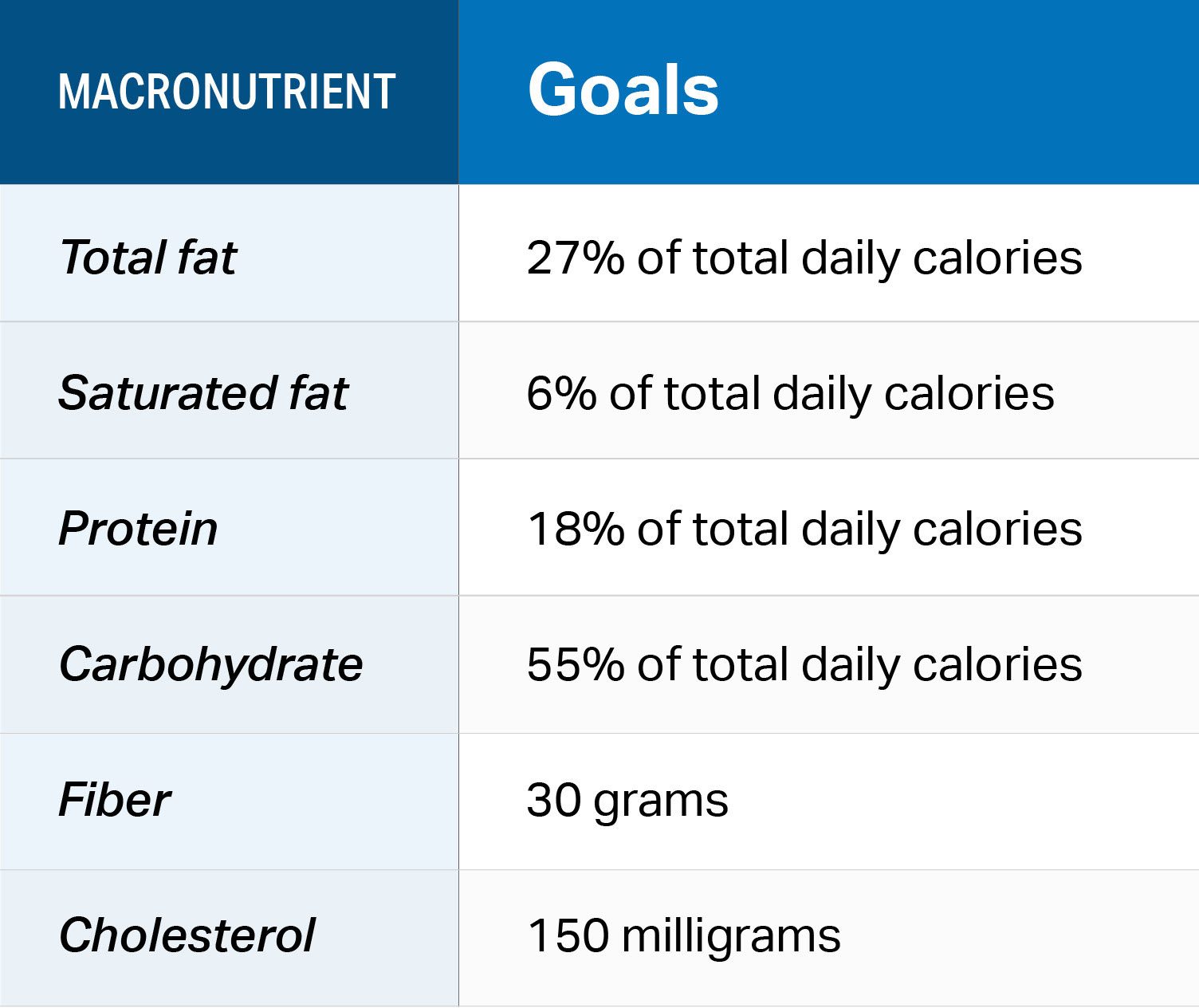
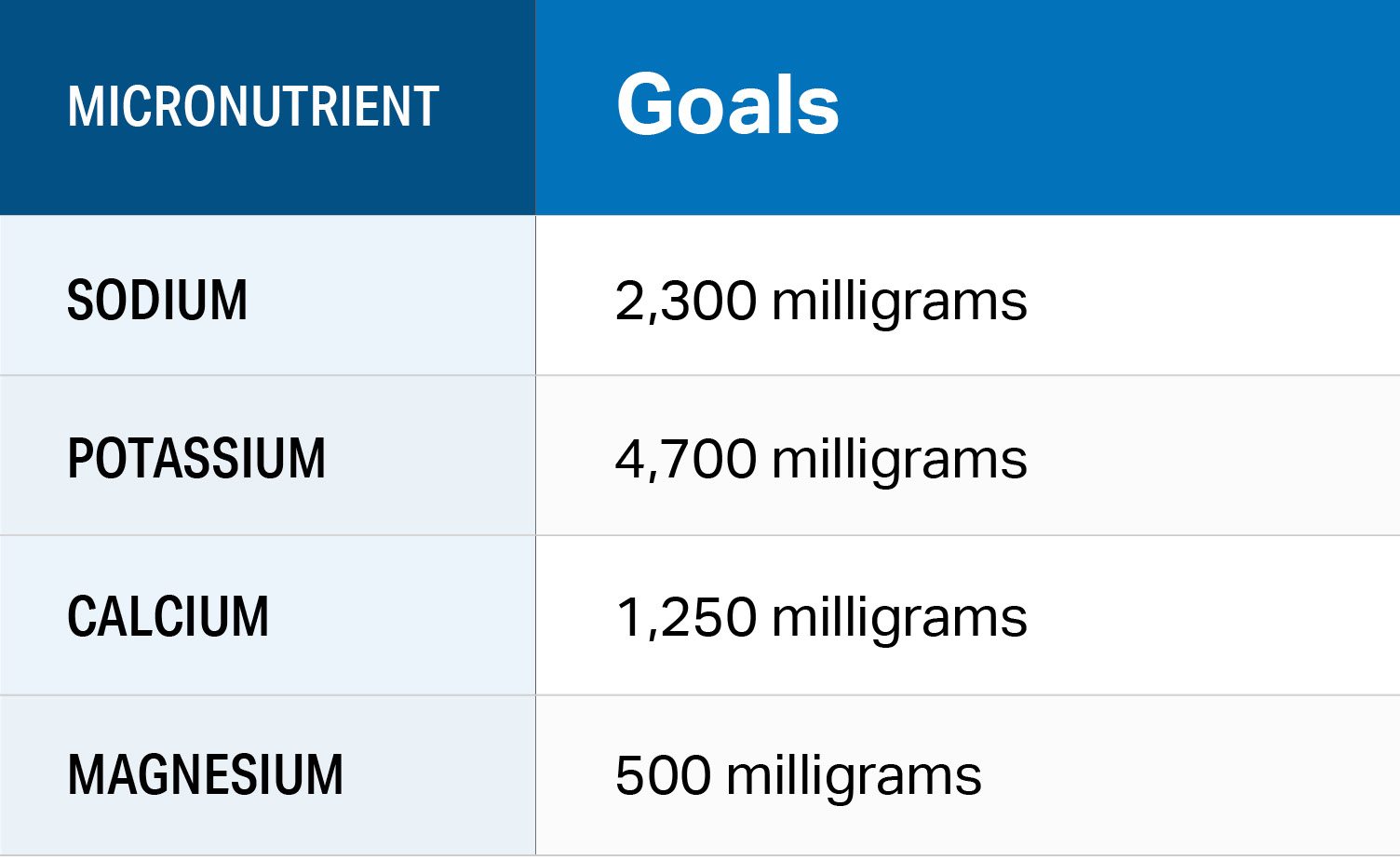
Chart adapted from the DASH Eating Plan Guide by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI).
In short, the DASH eating plan is sodium-controlled and emphasizes sensible food choices. Research shows it may help reduce blood pressure better than some medications.
THE LOWDOWN ON SODIUM
All of the above nutrients count, but sodium deserves a special callout as the nutrient most of us associate with high blood pressure. The DASH eating plan caps sodium at 2,300 milligrams, and even suggests going as low as 1,500 milligrams daily for better results. The downside is Americans are used to eating 3,400 milligrams per day, so easing back on sodium can deal a drastic blow to the taste buds.
It’s OK to cut back on salt slowly. Sodium matters, but so does potassium, calcium and magnesium. Eating more of these electrolytes can help balance the effects of sodium. Check out this Beginner’s Guide to Low-Sodium Eating for more practical tips.
FOOD RECOMMENDATIONS FOR DASH
While it may be easier to figure out which foods contain the DASH macronutrients of interest, it’s more difficult with micronutrients. Here’s a handy list for reference when planning to hit your DASH micronutrient goals:
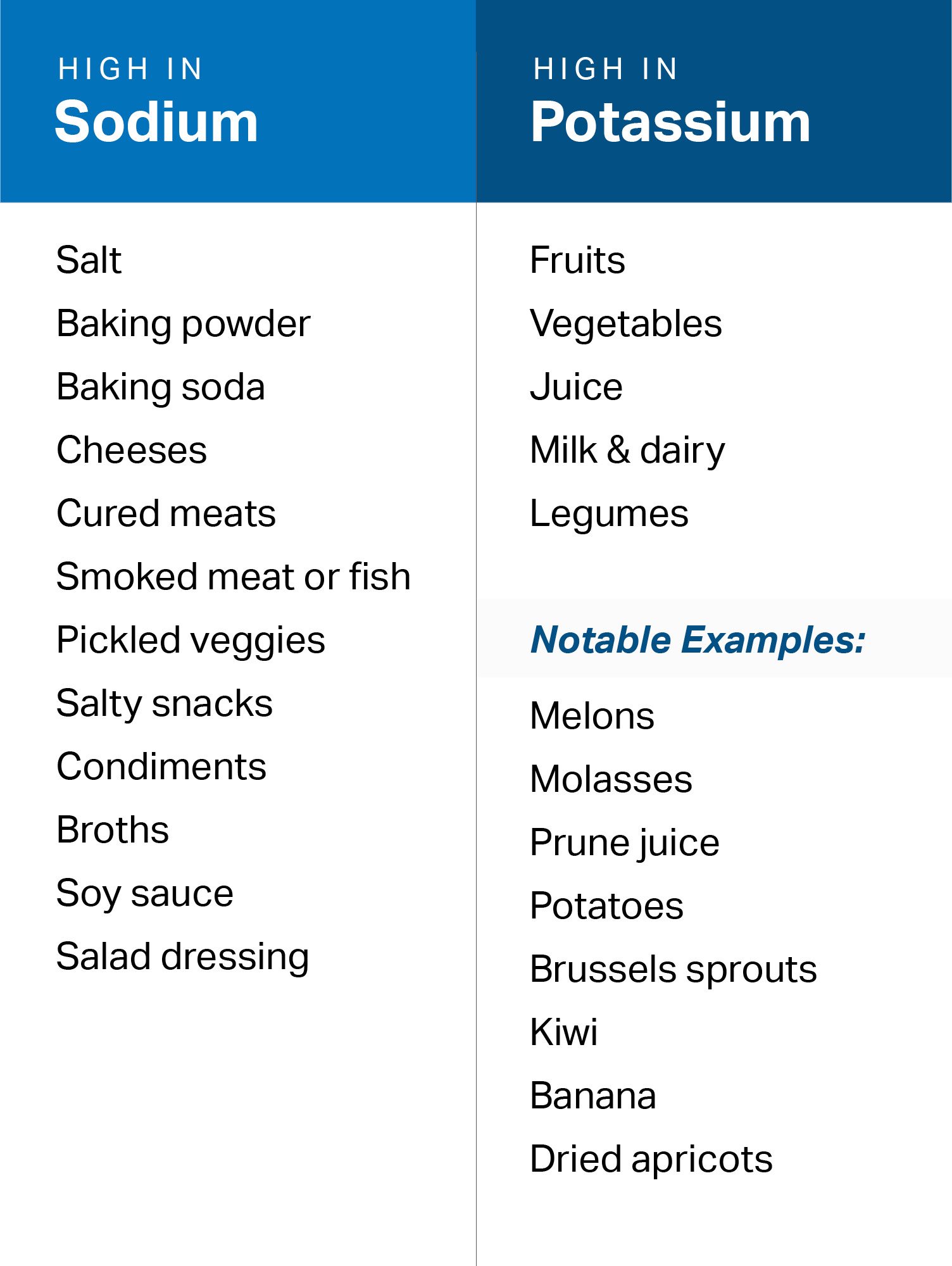

To get started on the DASH eating plan, check out two awesome resources here and here.
EXERCISE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR DASH
Everyone should strive for 150 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous exercise weekly. At this intensity, you should feel challenged. Examples of moderate-intensity exercises are walking briskly, bicycling at 10 miles per hour, ballroom dancing or gardening. Examples of vigorous intensity exercises are jogging, swimming, cycling at 10+ miles per hour or jumping rope.
THE TAKEAWAY
High blood pressure isn’t an immediate killer, but it’s a key contributor to heart disease, the leading cause of death in the U.S. and globally. This year the American Heart Association lowered its blood pressure guidelines. As a result nearly half of the U.S. adult population meets the criteria for high blood pressure. Hopefully they’ll do something about it. If you fall into this group, know that the DASH eating plan is a great place to start.
Have you tried the DASH eating plan before? Share your experience with others in the comments below.




